Protein linked to Alzheimer's, strokes cleared from brain blood vessels | The Source
In mice, antibody removes amyloid, improves vessel function without raising risk of brain bleeds
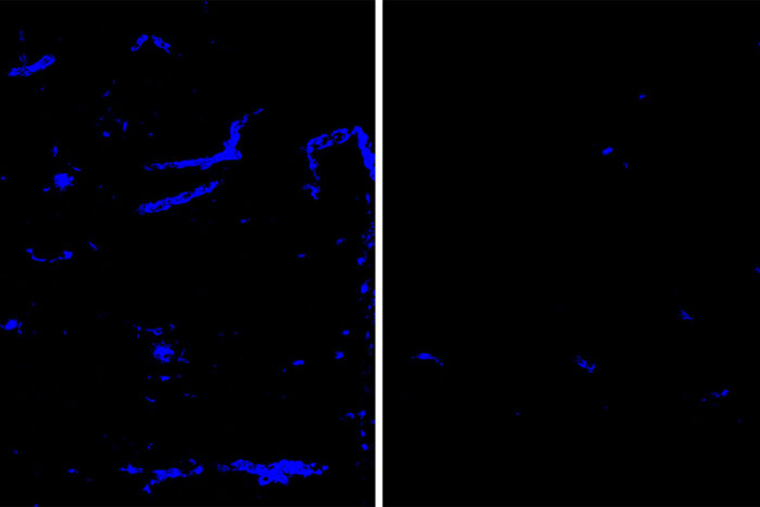
Amyloid deposits (blue) in mouse brain tissue and blood vessels are reduced after treatment with an antibody that targets the protein APOE (right), a minor component of amyloid deposits, compared to a placebo antibody (left). Amyloid deposits in the brain increase the risk of dementia and strokes. Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have identified an antibody that clears amyloid deposits from the brain without raising the risk of brain bleeds. (Image: Monica Xiong)
February 17, 2021
SHARE
As people age, a normal brain protein known as amyloid beta often starts to collect into harmful amyloid plaques in the brain. Such plaques can be the first step on the path to Alzheimer’s dementia. When they form around blood vessels in the brain, a condition known as cerebral amyloid angiopathy, the plaques also raise the risk of strokes.
Related Keywords
David Holtzman , Ralphg Dacey , Gretchenp Jones , Gregoryj Zipfel , Hongjiang , Monica Xiong , Department Of Neurosurgery , Department Of Neurology , Washington University School Of Medicine , Washington University School , Science Translational Medicine , Distinguished Professor , Neurological Surgery , டேவிட் ஹோல்ட்ஸ்மேன் , மோனிகா க்ஷ்ிொன் , துறை ஆஃப் நரம்பியல் அறுவை சிகிச்சை , துறை ஆஃப் நரம்பியல் , வாஷிங்டன் பல்கலைக்கழகம் பள்ளி ஆஃப் மருந்து , வாஷிங்டன் பல்கலைக்கழகம் பள்ளி , அறிவியல் மொழிபெயர்ப்பு மருந்து , புகழ்பெற்ற ப்ரொஃபெஸர் , நரம்பியல் அறுவை சிகிச்சை ,
comparemela.com © 2020. All Rights Reserved.